How a Data Center works
The data center is a highly protected industrial building, built with a very specific purpose in mind: to ensure that computer servers with digital applications run without interruption, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. This is because professional data centres use the latest innovations in data infrastructure, cooling, power supply, fire safety and security. All these systems are redundant, which means that all systems are equipped with back-up systems that take over if one of the systems fails.
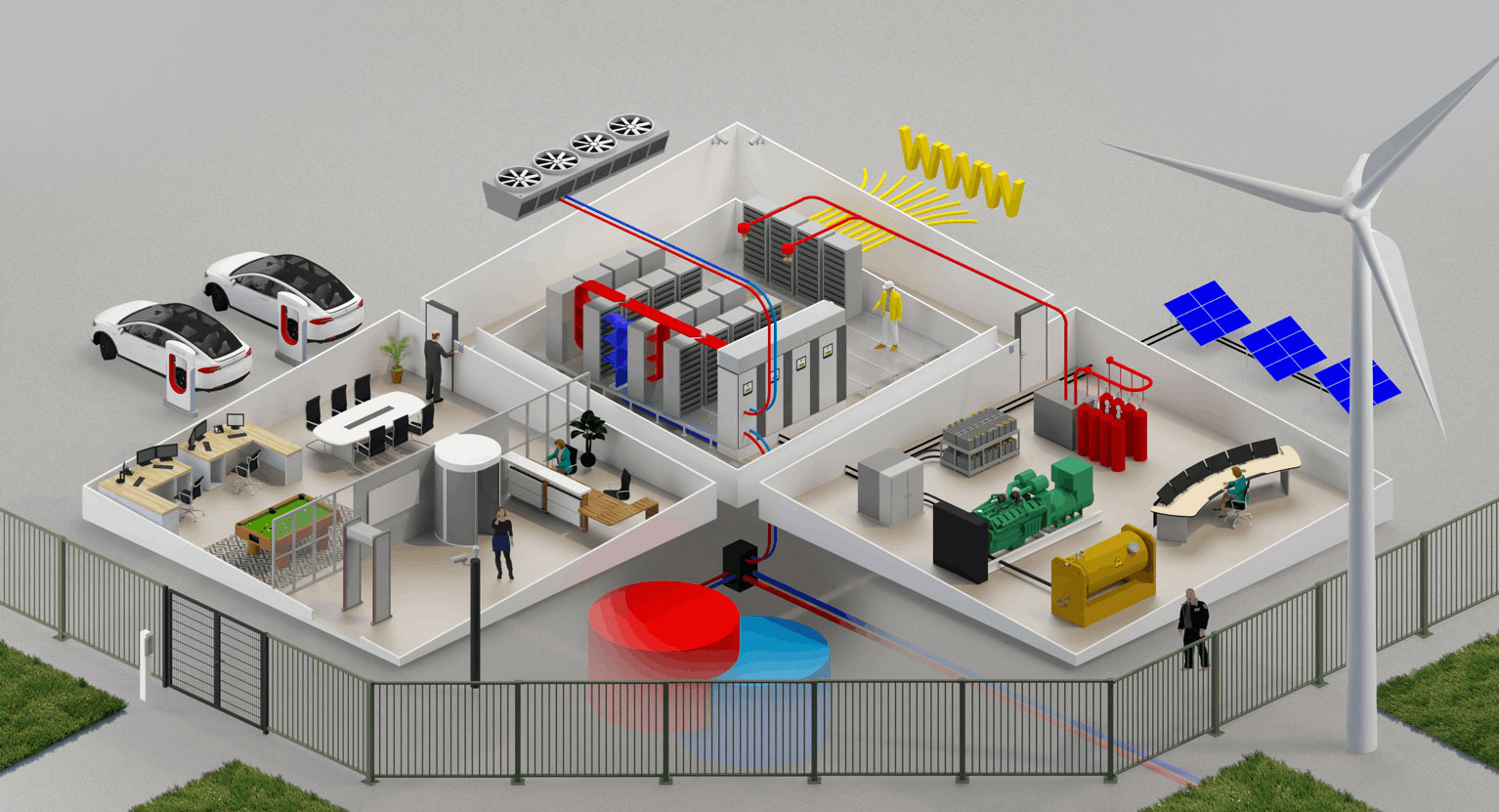
Server Room
In this highly secured room, the racks and servers of data center customers are housed. This room is fully air-conditioned, which means that the temperature and humidity are continuously regulated, to make sure that the servers cannot overheat or damage. The servers are usually interconnected by means of patch systems.
MeetMe Room
In this room, you can find the equipment of various network suppliers. These suppliers provide all connections between the servers in the server room and the World Wide Web (WWW). The connections used for this are redundant (duplicated) to ensure continuity of the connections, even in case of an outage.
Power Supply (UPS)
This system is the heart of the data center's energy supply. A data center usually runs on electricity, which is mostly generated sustainably. In some cases, a power outage may occur. When this happens, the UPS will ensure that the servers in the server room are nonetheless supplied with electricity. The procedure is as follows: immediately after a power failure, batteries will take care of the supply for a short time. Thanks to the batteries, the emergency power generator has enough time to warm up. From there on, it will take over the power supply until the power is back on.
Cooling system
This system ensures the cooling of the servers. Data centers often use outdoor cooling to remove warm air from the servers. This means that the heat is released to the outside air, while cooler air is brought in. In the Netherlands, free air cooling makes up 75% of the total amount. Only in case of very hot and humid days, additional water is needed to accelerate heat release through evaporation. One development that gains importance in the Netherlands, is the transport of the residual heat from servers to heat networks. This way, it can be used for the heating of homes and offices.
Physical Security
Physical security is vital to a data center. Due to the enormous amount of data stored on the servers, it is essential that only authorized people have access to certain parts of the facility. To guarantee this, data centers work with different security shells. The outer shell includes a fence that surrounds the premise, and the inner shell includes personnel locks and biometric access systems. Furthermore, most data centers employ professional security guards. They are the ears and eyes of the building.
Fire fighting system
A data center is designed to protect its people, equipment and (customer) data against fire hazards. Traditional fire fighting systems such as water and foam can potentially do more harm than good to the data center, as it damages the equipment and (customer) hardware. Therefore, it is equipped with a gas extinguishing system that can immediately release a gas mixture at the slightest detection of smoke. This way, any escalation related to fire is avoided.
Network Operations Center (NOC)
In the NOC, the various business-critical processes and systems in the data center are continuously monitored via a BMS or via DCIM software. This way, predictive maintenance can take place. Furthermore, the staff can act promptly in case of outages and incidents in energy, cooling, or connectivity.
Energy supply
Electricity is the most important fuel for data centers. Precisely for this reason, data centers are built to be efficient, as less electricity results in lower cost. A no-brainer! The bigger part of the electricity is used for customer equipment. The remaining part is used for facilitating equipment such as cooling and ventilation. Most data centers have green power contracts with their energy suppliers, and large data centers usually set up Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) in collaboration with wind parks.
Aquifer thermal energy storage (ATES)
With an ATES, data centers can store cold and hot water in the ground. On hot summer days, the cold groundwater is extracted from the ATES and used for cooling by means of a heat exchanger. In winter, the hot groundwater can be used for the heating of nearby facilities such as homes, schools and offices.
Offices and meeting rooms
Data centers want to ensure a pleasant environment for their employees. Especially since the technical staff and security guards sometimes work in the evening and at night, special attention is paid to a positive experience with plenty of comfort. In addition to that, there are facilities for customers, suppliers and other visitors such as the lobby, canteen, workplaces and meeting rooms.